Australia has a tale about its rabbit population that’s full of unexpected turns and fascinating details! Initially brought in for sport hunting purposes; these cute bunnies rapidly evolved into one of the continents abundant and problematic species.

An Overview of the Past
The story of Australias rabbits dates back to 1859 when Thomas Austin introduced 24 rabbits (Oryctolagus cuniculus) to his land in Victoria with the purpose of creating a hunting activity for leisure on his property.
The Infestation of Rabbits
The exponential increase in rabbit populations in Australia posed farming issues. Rabbits are plant eating animals with a voracious appetite for greenery. Quickly started to overeat vegetation causing harm to indigenous flora and vying with livestock for sustenance. Consequently, impacting soil health and triggering erosion. The severity of the scenario was such that it was labeled the “rabbit plague.”


Different strategies were tried to manage the rabbit population in Australia such as hunting and introducing predators like foxes or using poison. They didn’t work enough as expected. In the 1950s success came with the use of the virus which had a major impact on reducing rabbit numbers. Then in the 1990s another virus called Rabbit Hemorrhagic Disease (RHD) was used to control their population. However, rabbits continue to be a presence in Australia till today despite these efforts.
Distinctive Adjustments
In Australia rabbits are intriguing not for their past but for their distinct qualities! Lets delve into some facts and standout traits of these creatures.
Rabbits reproduce rapidly as a single pair can have, up to 30 babies in a year! Female rabbits can get pregnant after giving birth which helps them multiply quickly and grow their population.
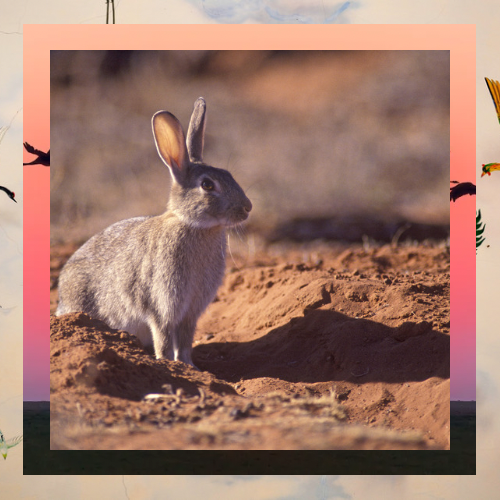
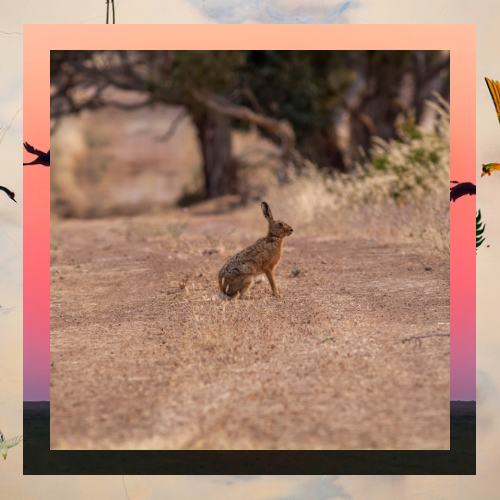


Rabbits have an impact due to their knack for changing ecosystems by creating complex underground tunnels known as warrens that can lead to soil erosion and impact the growth of plants in the area.
In Australia’s wilds roam creatures like dingoes and eagles that hunt rabbits alongside cats as predators. Enough these predators have not managed to keep the rabbit population at bay.
Rabbits primarily eat grasses and plants such as leaves and bark since they are herbivores by nature. Can adjust to habitats in Australia due to their varied diet preferences.
In their habitat rabbits usually survive for about 1 to 10 years. They can live, up to 10 years when in captivity. Their short lifespan outdoors is because of predators and diseases.


Interesting Tidbits About Rabbits in Australia
After the myoxma virus was introduced and caused a decrease in rabbit numbers initially, some rabbits managed to develop immunity over time leading to a recovery in their populations.
Warren Ponders, a rabbits burrow can be quite intricate and elaborate with entry and exit points for safety from predators and adverse weather conditions.
Rabbits in Australia are not just seen as pests; they have played a role in the countrys economy by being valuable for their fur and meat industries. Rabbit meat was even referred to as ” mutton”. Was a popular choice during the Great Depression era.


The Continuing Struggle
Despite attempts to manage their population growth in Australia rabbits remain an issue in the country. They show resilience and adaptability to changing circumstances, which calls for research and effective strategies to minimize their impact within the ecosystem.
In summary
The tale of rabbits in Australia serves as an example of the outcomes that arise when foreign species are brought into a different habitat. Their quick expansion and the environmental issues they bring about have significantly impacted the scenery. Exploring their background and traits not sheds light on the intricacies of wildlife conservation. Also emphasizes the significance of safeguarding indigenous ecosystems.
This article provides a glimpse into the fascinating world of Australia’s rabbits, exploring their unique traits and the challenges they present. The ongoing efforts to manage their populations reflect the complex interplay between humans and the natural world..






Good shout.