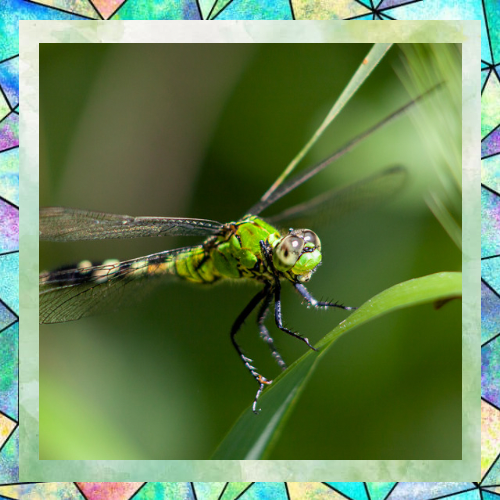
Dragonflies are among the most fascinating creatures in the insect world. With their shimmering wings, vibrant colors, and incredible flying abilities, they capture the imagination of anyone lucky enough to observe them. These insects have been around for over 300 million years, predating even the dinosaurs. Today, they continue to thrive in diverse habitats, from ponds and lakes to forests and meadows. Let’s take a closer look at these remarkable insects and uncover some of their unique traits and behaviors.
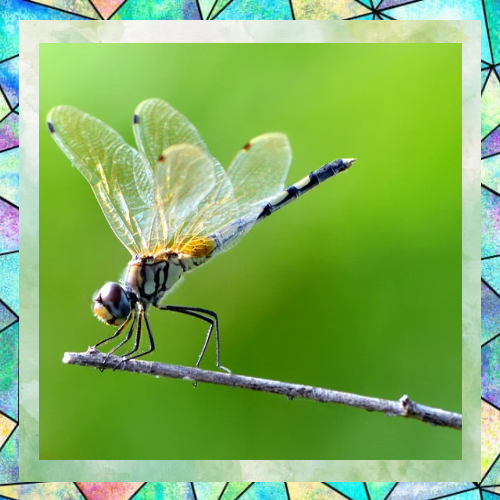
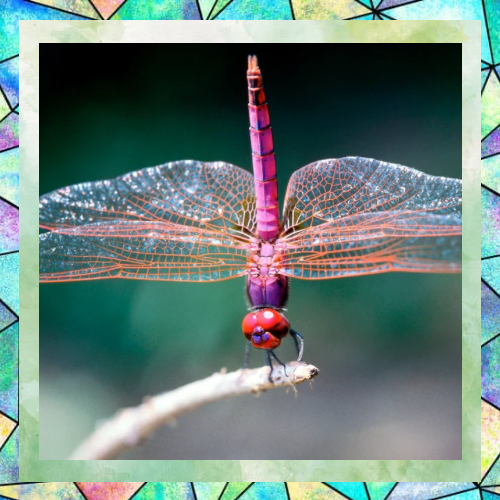


Masters of Flight
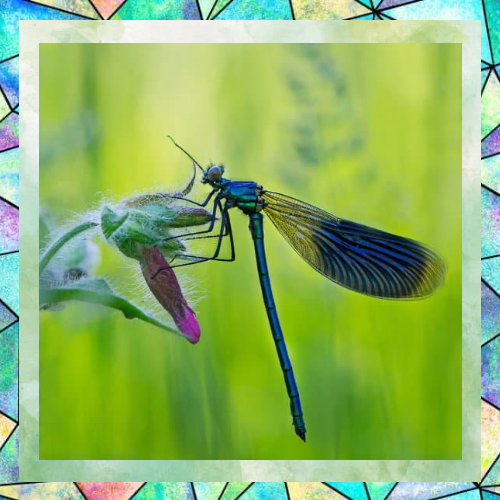
Dragonflies are renowned for their flying skills. They can hover, fly backward, and change direction in an instant. Their four wings operate independently, allowing them to perform maneuvers that would make even the most advanced aircraft envious. They can reach speeds of up to 30 miles per hour, making them one of the fastest flying insects. Their agility in the air is not just for show—it helps them catch prey and evade predators with ease.
Predatory Prowess
Dragonflies are fierce predators, both as adults and in their larval stage. As adults, they feed on other flying insects, such as mosquitoes, flies, and even smaller dragonflies. They catch their prey mid-air using their legs, which are specially adapted to form a basket-like structure. Their larvae, known as nymphs, live in water and are equally voracious. They hunt tadpoles, small fish, and aquatic insects, using extendable jaws to snatch their meals.
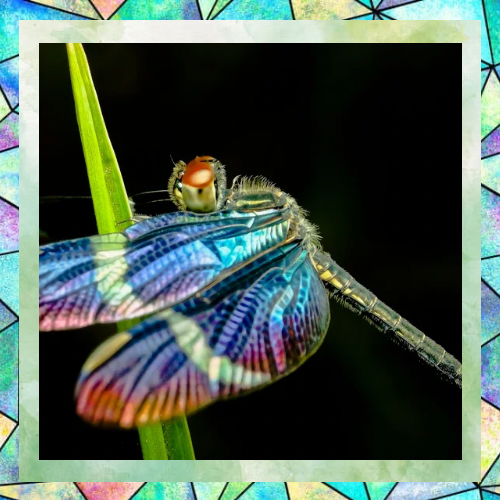
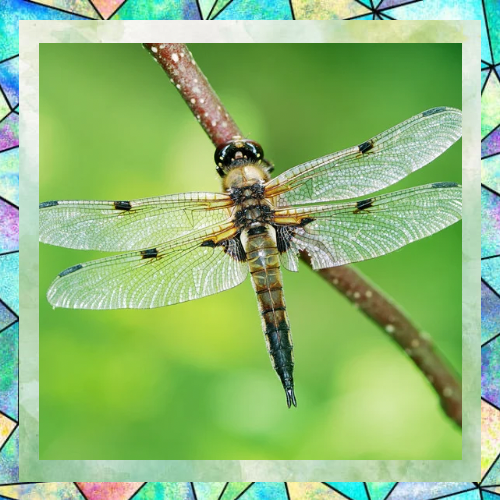


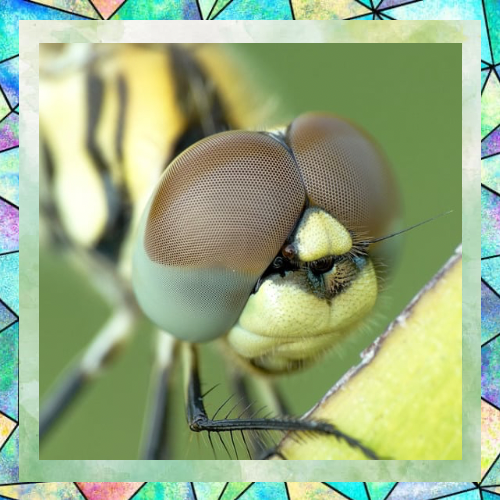
Eyes Like No Other
One of the most striking features of dragonflies is their large, compound eyes. Each eye contains up to 30,000 facets, giving them nearly 360-degree vision. This exceptional eyesight helps them detect movement and spot prey from a distance. Their eyes are so sensitive that they can see colors beyond the range of human vision, including ultraviolet light. This visual acuity is crucial for their hunting success and survival.
Not Walking Legs
Dragonflies are fascinating insects known for their agile flight and striking appearance. One interesting aspect of dragonflies is that their legs are not well-suited for walking. Here’s why:
1. Specialized for Perching and Capturing Prey: Dragonfly legs are primarily adapted for perching and grasping rather than walking. They have strong, spiny legs that are excellent for clinging to surfaces like leaves or stems. These legs are also used to capture and hold prey while in flight.
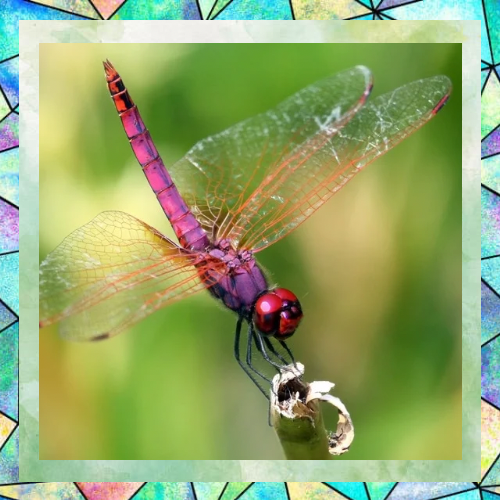
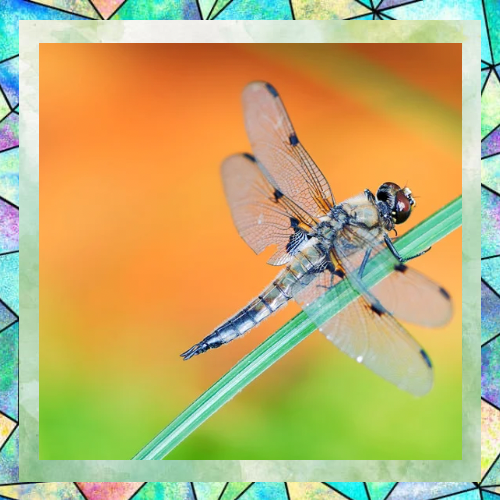


2. Positioning of Legs: Dragonflies have six legs, but their legs are positioned in a way that makes walking inefficient. The legs are located close to the front of their body, which is ideal for snatching prey mid-air but not for walking on the ground.
3. Lack of Mobility: Dragonfly legs are not designed for the kind of joint movement required for walking. Their legs are more rigid and optimized for quick, precise movements to grab prey or stabilize themselves during flight
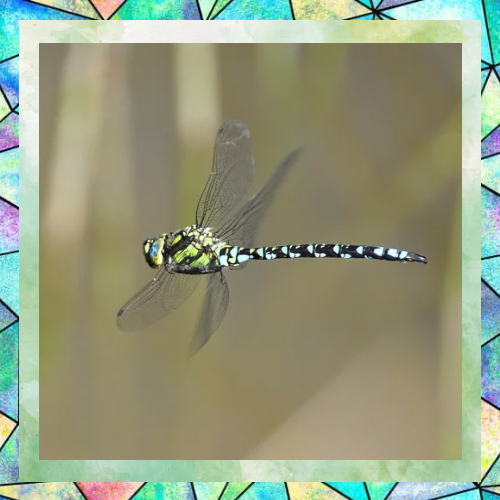
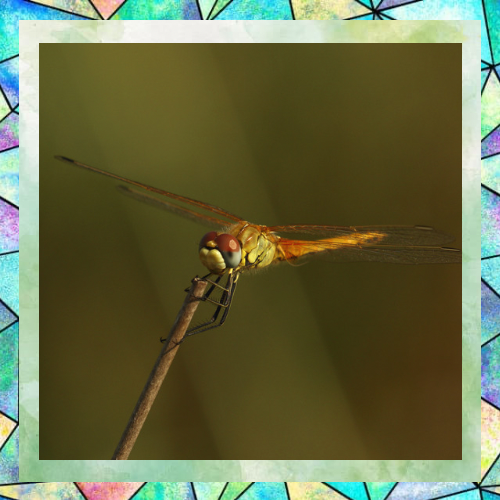


4. Flight-Centric Lifestyle: Dragonflies are highly aerial insects, spending most of their time flying. Their legs play a secondary role to their wings, which are their primary means of movement. Walking is simply not a significant part of their daily activities.
5. Evolutionary Adaptation: Over millions of years, dragonflies have evolved to prioritize flight and hunting efficiency over terrestrial locomotion. Their legs have become specialized tools for their predatory lifestyle, rather than for walking.
Dragonflies cannot walk because their legs are adapted for perching, grasping prey, and stabilizing during flight. Their evolutionary design prioritizes aerial agility over terrestrial mobility, making them masters of the air but not of the ground.
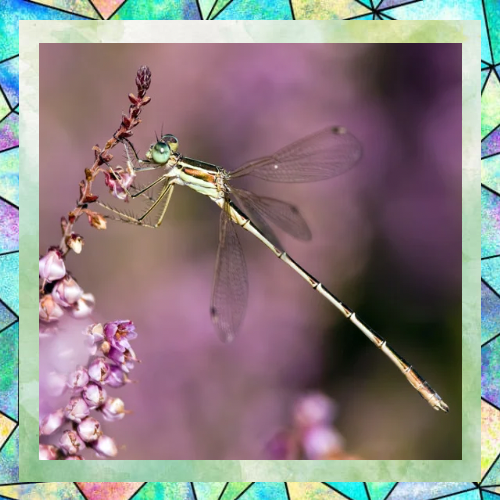
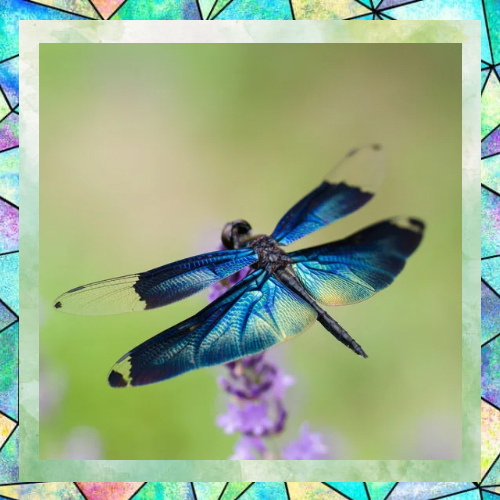


A Life of Transformation
Dragonflies undergo a remarkable life cycle that includes three stages: egg, nymph, and adult. Females lay their eggs in or near water, and once hatched, the nymphs spend most of their lives underwater. This stage can last anywhere from a few months to several years, depending on the species. When the time comes, the nymph climbs out of the water, sheds its exoskeleton, and emerges as a fully formed adult. This process, known as metamorphosis, is a testament to the resilience and adaptability of these insects.
Ancient Flyers
Dragonflies have been around since the Carboniferous period, over 300 million years ago. Fossils of ancient dragonflies, such as Meganeura, reveal that some species had wingspans of up to 28 inches—making them the largest insects to ever exist. While modern dragonflies are much smaller, they retain many of the characteristics that made their ancestors so successful.
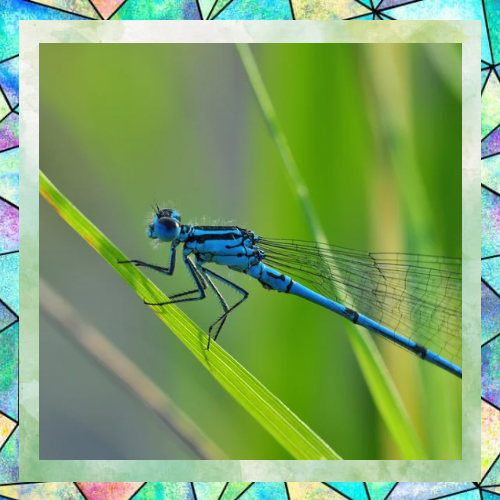
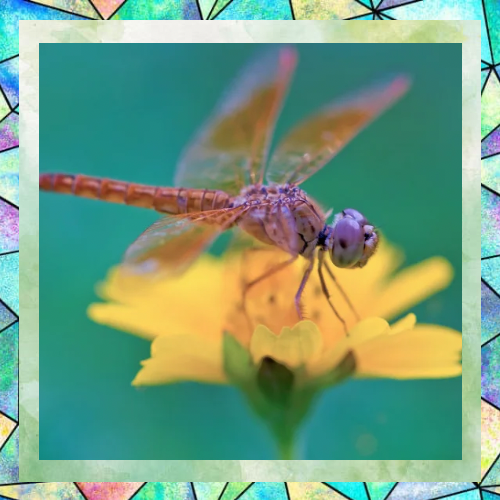


Fun Facts About Dragonflies
- Dragonflies can fly straight up and down, as well as hover in place, much like a helicopter.
- They are often called “devil’s darning needles” in folklore, though they are harmless to humans.
- Dragonflies are found on every continent except Antarctica.
- Some species migrate long distances, traveling thousands of miles in search of suitable habitats.
- Their wings are covered in tiny veins that provide strength and flexibility, allowing them to withstand strong winds.
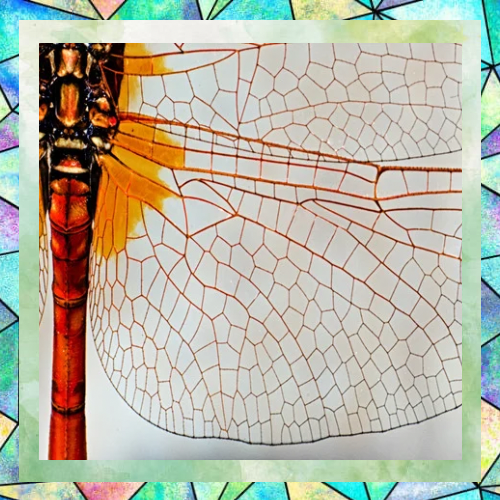
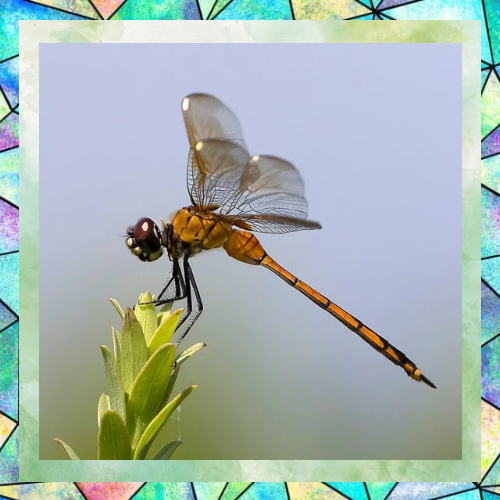


Ecological Importance
Dragonflies play a vital role in ecosystems. As predators, they help control populations of insects, including pests like mosquitoes. Their presence in an area is often an indicator of a healthy environment, as they require clean water to breed. By maintaining balanced insect populations, dragonflies contribute to the overall health of their habitats.
Threats and Conservation
Despite their resilience, dragonflies face threats from habitat loss, pollution, and climate change. Wetlands, which are crucial for their reproduction, are disappearing at an alarming rate. Conservation efforts, such as protecting wetlands and reducing pesticide use, are essential to ensuring the survival of these ancient insects.


Conclusion
Dragonflies are more than just beautiful insects—they are skilled hunters, ancient survivors, and important contributors to their ecosystems. Their incredible flying abilities, unique life cycle, and ecological significance make them a subject of endless fascination. By learning more about these aerial acrobats, we can better appreciate the intricate web of life that surrounds us.
References
- Corbet, P. S. (1999). Dragonflies: Behavior and Ecology of Odonata. Cornell University Press. https://www.academia.edu/1066050/Dragonflies_behaviour_and_ecology_of_Odonata
- Paulson, D. (2011). Dragonflies and Damselflies of the East. Princeton University Press. https://rinhs.org/review-dragonflies-damselflies-east/
- National Geographic. (n.d.). Dragonfly Facts. https://www.nationalgeographic.com/animals/invertebrates/facts/dragonflies-insects
- Smithsonian Magazine. (2020). The Secret World of Dragonflies. https://www.smithsonianmag.com/science-nature/14-fun-facts-about-dragonflies-from-their-lethal-hunting-prowess-to-incredible-migratory-feats-96882693/