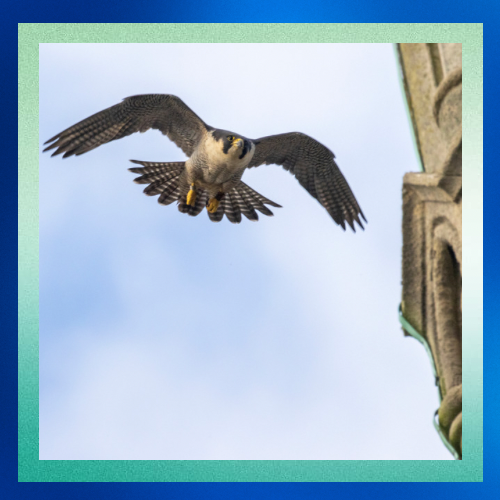
In the world of birds of prey, few command the skies with the awe-inspiring prowess of the peregrine falcon (Falco peregrinus). From its remarkable hunting abilities to its astonishing speed, this magnificent raptor has captivated the imagination of bird enthusiasts and scientists alike. Join me as we delve into the thrilling world of the peregrine falcon.
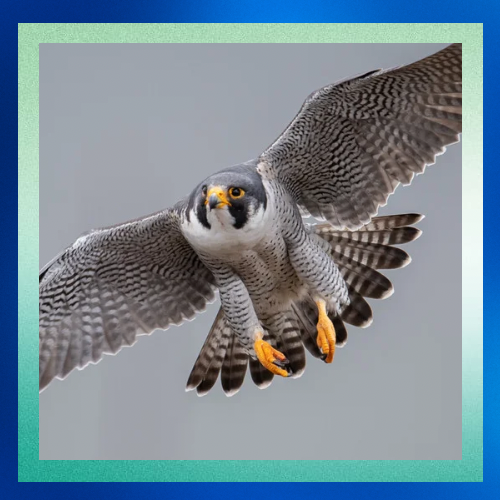
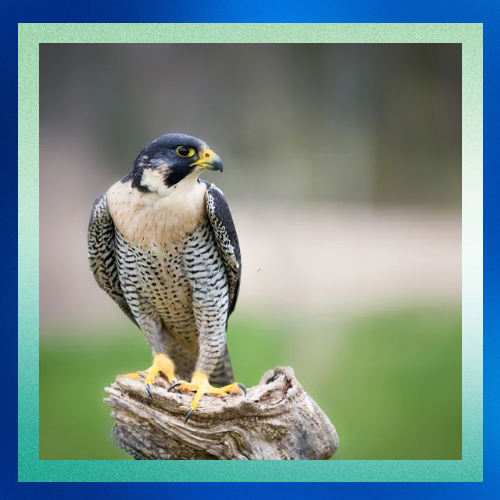


Majestic Hunters
The peregrine falcon is renowned for its exceptional hunting skills. With a streamlined body and sharp, curved talons, it’s a master of aerial pursuit. Peregrines primarily feed on other birds, often catching them mid-flight with incredible precision and agility. Their hunting strategy involves high-speed dives, known as stoops, where they can reach speeds of over 240 miles per hour (386 kilometers per hour) as they descend upon their prey.
Adaptations for Speed
What makes the peregrine falcon such a speed demon? One key factor is its aerodynamic design. These birds have long, pointed wings and a slender body, perfect for slicing through the air with minimal resistance. Additionally, peregrines possess specialized respiratory and cardiovascular systems that enable them to maintain high speeds during pursuit without tiring easily.
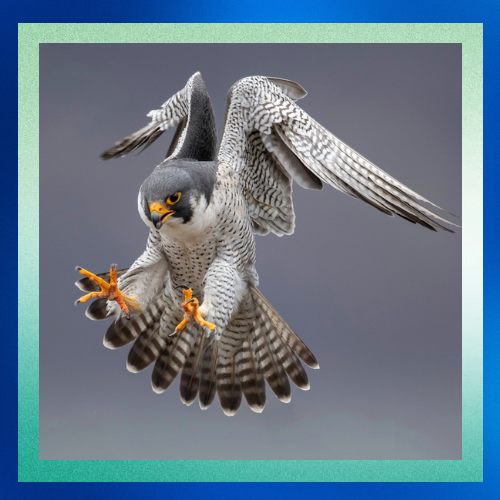
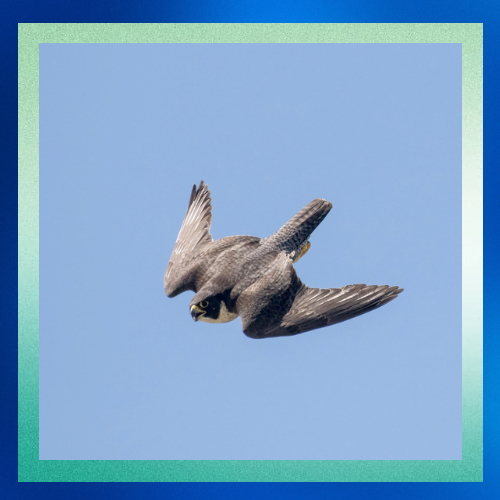


Key Respiratory Adaptations
1. Efficient Oxygen Exchange
• Like all birds, peregrine falcons possess a unique respiratory system involving air sacs in addition to lungs. This system enables a continuous flow of fresh air through the lungs during both inhalation and exhalation, maximizing oxygen exchange.
• The lungs themselves are highly efficient, with fine capillary networks that allow for rapid diffusion of oxygen into the bloodstream.
2. Large Heart and High Oxygen Transport
• The peregrine falcon has a large, powerful heart relative to its body size, which pumps oxygen-rich blood to its muscles with great efficiency.
• Hemoglobin in its blood binds oxygen effectively, ensuring the bird has ample oxygen during sustained high-speed chases.
3. High Breathing Rate
• During flight, particularly at high speeds, the falcon increases its breathing rate to ensure sufficient oxygen intake. This adaptation supports the energy demands of rapid wingbeats and intense muscle activity.
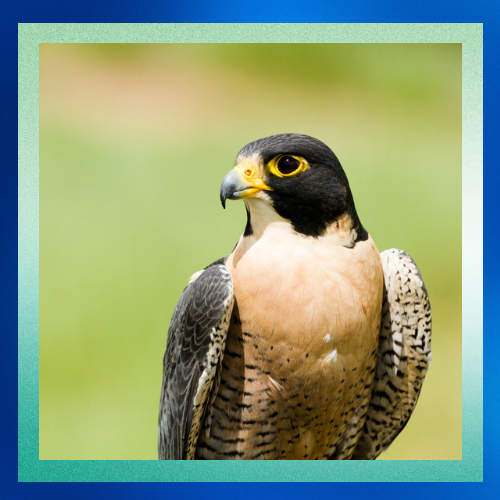
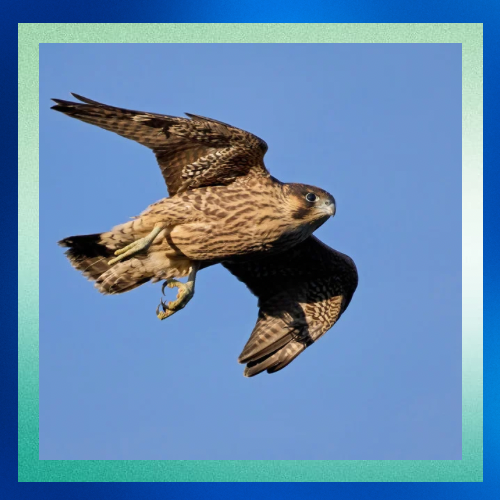


4. Nasal Adaptations for High-Speed Flight
• At extreme speeds, the air pressure entering the falcon’s nostrils can become overwhelming. To manage this, peregrine falcons have bony tubercles (small projections) inside their nostrils. These structures reduce and regulate the airflow, ensuring that air enters the respiratory system at a manageable pressure.
• Without these adaptations, the rapid airflow could damage the bird’s lungs or disrupt breathing.
5. Low Susceptibility to Hypoxia
• Peregrine falcons often hunt at high altitudes, where oxygen levels are lower. Their respiratory system allows them to efficiently extract oxygen even in these conditions, preventing hypoxia (oxygen deficiency).
Role of the Respiratory System in Hunting
• During a stoop, the peregrine falcon experiences enormous physical demands, including increased resistance from high-speed air. The respiratory system works in tandem with its muscular and cardiovascular systems to deliver oxygen and eliminate carbon dioxide efficiently.
• This allows the falcon to maintain focus, control its descent, and recover quickly after a hunt.
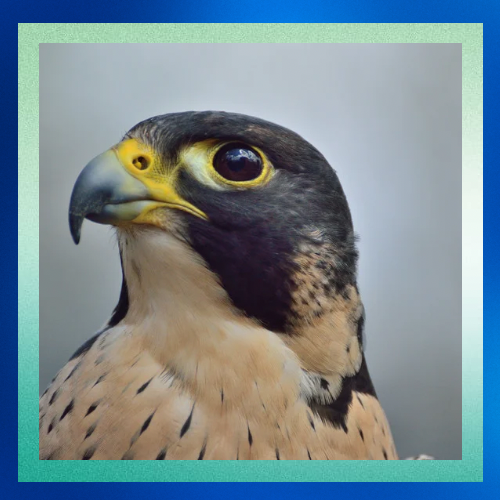
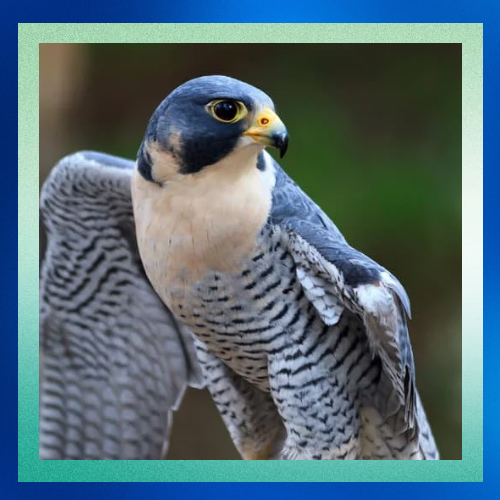


Global Distribution
Peregrine falcons have a vast global distribution, found on every continent except Antarctica. They inhabit diverse habitats ranging from coastal cliffs and mountainous regions to urban areas. In cities, they often nest on skyscrapers and bridges, adapting remarkably well to human landscapes.
Conservation Success Story
The peregrine falcon’s journey has not been without challenges. In the mid-20th century, their populations plummeted due to widespread use of pesticides like DDT, which led to eggshell thinning and reproductive failures. However, thanks to dedicated conservation efforts including bans on harmful chemicals and reintroduction programs, peregrine falcons have made a remarkable comeback. Today, they are considered a conservation success story, with populations rebounding in many regions.
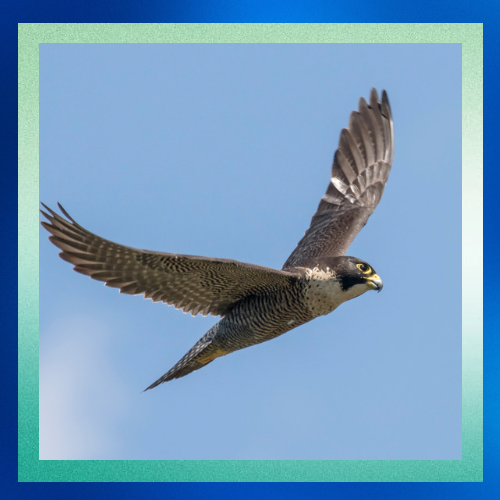
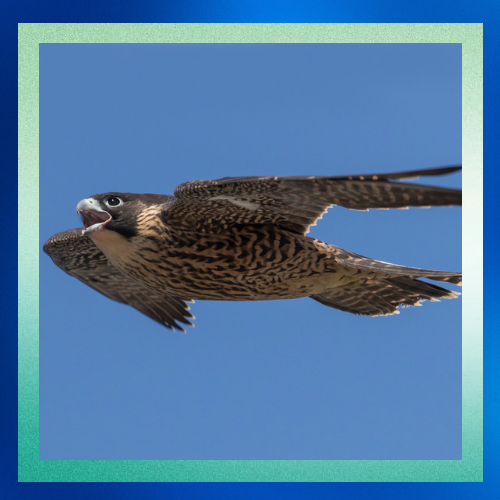


Fascinating Behavior
Beyond their hunting prowess, peregrine falcons exhibit intriguing behaviors. They are known for their spectacular courtship displays, which involve high-speed aerial acrobatics. During nesting season, pairs perform elaborate rituals, often involving mutual flights and vocalizations.
Peregrines are also fiercely territorial, defending their nesting sites from intruders with remarkable tenacity. Their piercing calls echo across the cliffs and canyons they call home, serving as a testament to their presence in the wild.
A Symbol of Freedom
Throughout history, the peregrine falcon has symbolized freedom and power. Revered by falconers and admired by bird watchers, these birds embody the untamed spirit of the wild. Their swift flight and unwavering gaze inspire artists, poets, and adventurers alike.
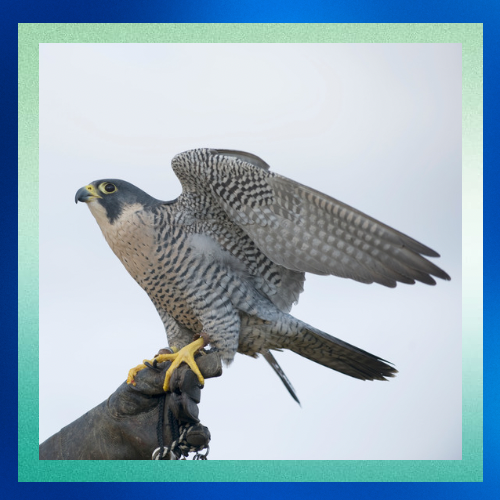
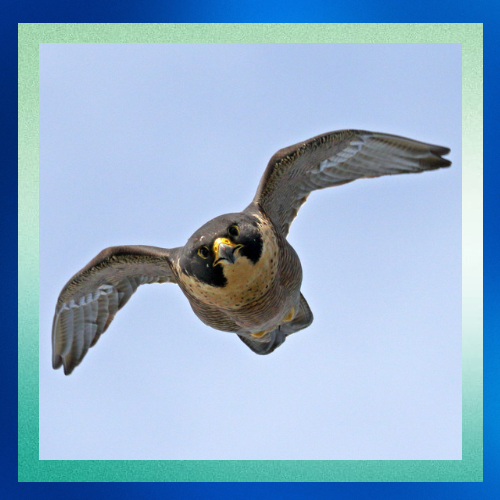


Conclusion
In conclusion, the peregrine falcon stands as a testament to nature’s ingenuity and resilience. With its unparalleled speed, exquisite hunting prowess, and adaptability, this raptor continues to captivate and inspire. As we strive to protect our planet’s biodiversity, the story of the peregrine falcon serves as a reminder of what we stand to gain when we work together to preserve our natural heritage.
References
1. National Geographic – Peregrine Falcon Overview. https://www.nationalgeographic.com/animals/birds/facts/peregrine-falcon
2. Cornell Lab of Ornithology – All About Birds: Peregrine Falcon. https://www.allaboutbirds.org/guide/Peregrine_Falcon/overview
3. The Peregrine Fund – Peregrine Falcon Fact Sheet. https://peregrinefund.org/explore-raptors-species/falcons/peregrine-falcon