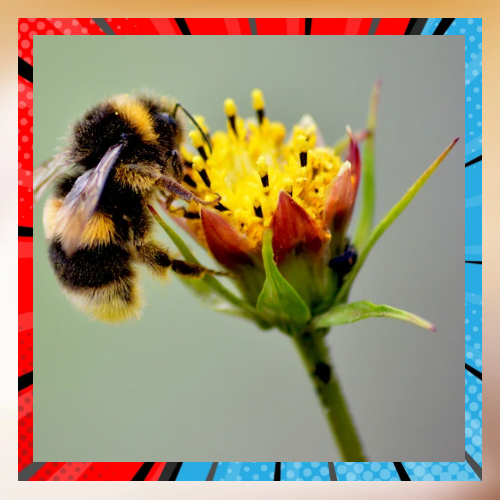
Pollinators are often overlooked champions in our ecosystems and farming industry. Ranging from bees and butterflies to birds and bats. These incredible beings have an impact in the propagation of flowering plants like crops that are crucial for human nutrition needs. Yet these valuable pollinators are encountering dangers due to habitat destruction, pesticides use, changing climate conditions and disease outbreaks. Recognizing their significance and the obstacles in their path is the stride, toward safeguarding and championing these creatures. This article delves into the role of pollinators and the challenges they face well, as the steps we can take to safeguard their existence.
The Important Role of Pollinators
The benefits provided to natures ecosystems. Pollinators play a role, in maintaining the balance of ecosystems by helping around 75% of flowering plants reproduce effectively and supporting a range of wildlife in the process.They assist in transferring pollen between flowers to aid in seed and fruit production for perpetuating plant species.
In forests and meadows as well as in wetlands, pollinators play a key role in enhancing biodiversity by helping various plant species to thrive. This diversity is vital for ecosystems that can endure challenges and offer important functions like storing carbon, purifying water, and keeping soil in place.


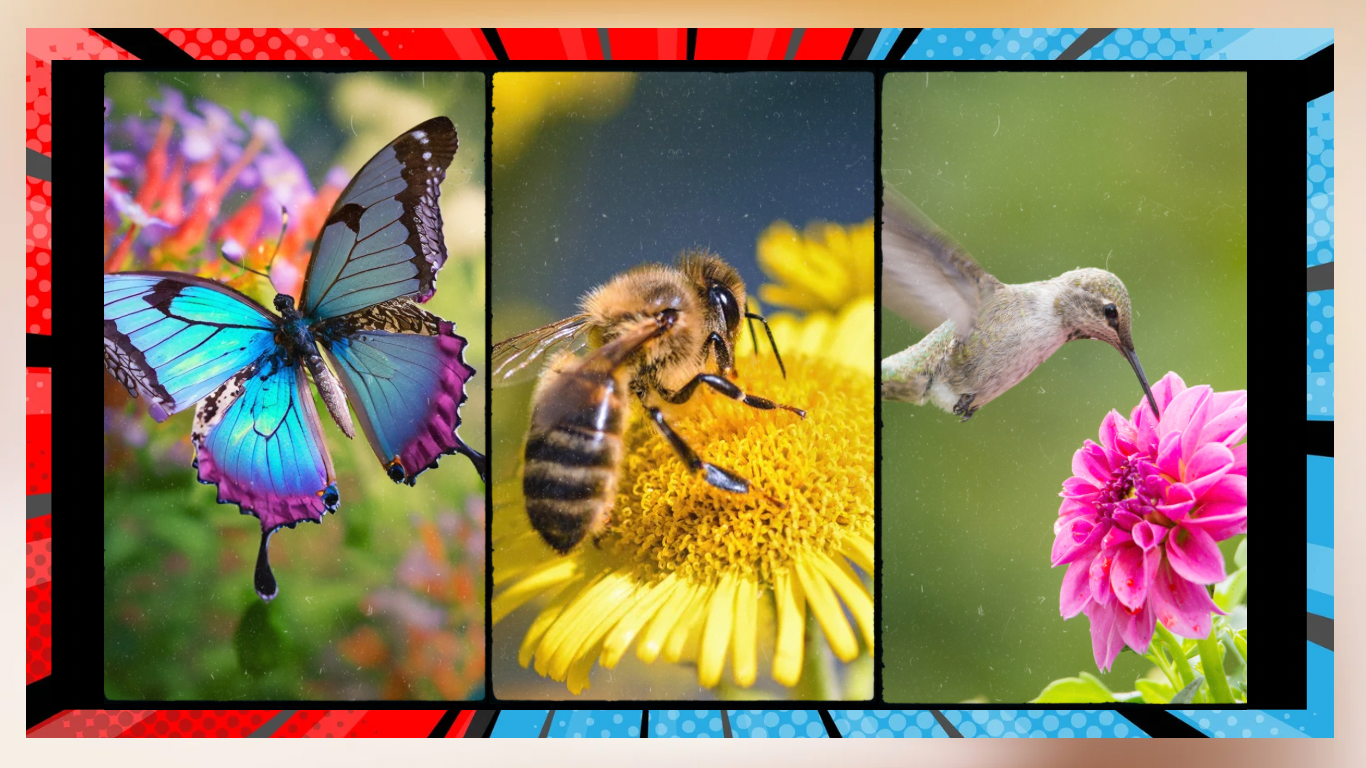
Enhancing output. In farming and cultivation practices pollinators play a role in the growth of crops globally. A significant portion of the worlds food supply, 35% to be precise depends greatly upon pollination for production; this includes a wide range of food items such as fruits, veggies, nuts, and seeds. Among the important crops are apples, almonds, blueberries, and tomatoes, all of which greatly rely upon pollinators to ensure optimal yield and quality.
Pollinators play a role, in enhancing productivity by not only boosting crop yields but also enhancing the quality of produce itself. For instance: Fruits that have been effectively pollinated tend to be bigger in size and more consistent. They also exhibit better taste and nutritional value. The economic significance of pollinators, in supporting agriculture is estimated to reach hundreds of billions of dollars every year.
The Challenges Facing Pollinators
The disappearance of habitats. One of the dangers to pollinators is the loss of their habitats caused by development and expansion of agriculture and deforestation activities. When natural environments are transformed into areas or used for farming and industries purposes, pollinators struggle to find the plentiful food sources essential for their survival. Additionally, fragmented habitats pose challenges to pollinators in locating spots and partners for mating leading to a decline in their numbers.
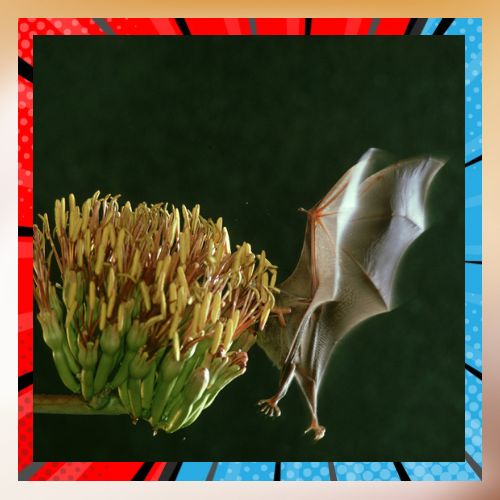


The use of pesticides. The extensive application of pesticides in farming presents a danger to pollinators. It is critical to note that insecticides like neonicotinoids can prove harmful to bees and other pollinators by impacting their foraging patterns, navigation abilities, and reproductive functions, minimal amounts of these substances can weaken the immune systems of pollinators thereby increasing their vulnerability to illnesses and parasites.
Climate change. Climate change is causing changes in where plants and pollinators are found and affecting how they interact with each other. The timing of when plants bloom can change due to shifts in temperature and rainfall patterns which can lead to mismatches between when flowers bloom and when pollinators are out and about. Moreover, extreme weather events like droughts or floods can harm pollinator populations directly as the places they call home.
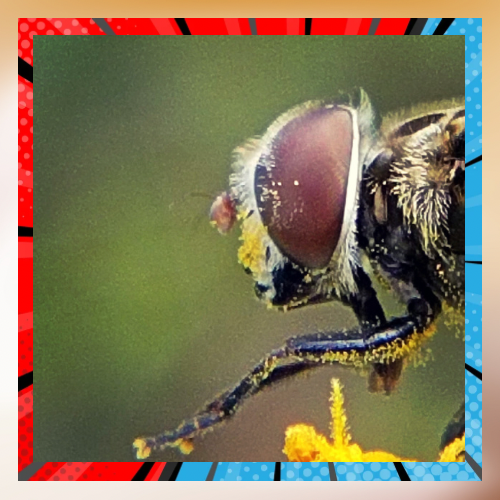
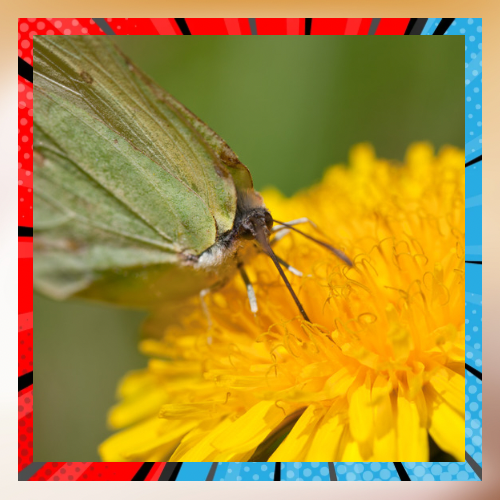


Pests. Bees and other pollinators face challenges from diseases and parasites, like the Varroa mite that harm honeybees by making them weaker and spreading viruses. Nosema and fungal infections are pathogens that can devastate pollinator communities and worsen their population decline.
Caring for Nurturing Pollinators
Revitalizing Natural Environments. It is crucial to protect and maintain environments to help pollinators thrive effectively in their habitats. One way to do this is by developing landscapes that are welcoming to pollinators and offer a variety of food sources all year round. By planting flowers and setting up wildflower fields while also preserving hedgerows and other natural elements we can form a range of habitats that cater to different types of pollinators.
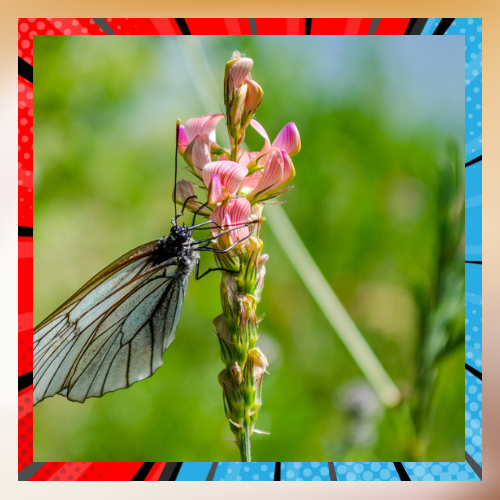


Practices promoting term balance and productivity in agriculture. Enabling farming methods can greatly lessen the effects of agriculture on pollinators.The utilization of Integrated Pest Management (IPM) which aims to limit the usage of pesticides along, with embracing organic farming techniques can establish more secure surroundings for pollinators. Additionally, farmers have the option to introduce techniques like crop rotation cultivating cover crops and reducing tillage to improve soil quality and offer shelters for pollinators.
Strategies to Address Climate Change. Taking action on climate change is essential for the lasting well being of pollinators. By cutting down on greenhouse gas emissions and shifting to renewable energy sources while focusing on energy efficiency practices we can lessen the effects of climate change. Moreover, preserving and rejuvenating carbon storage areas like forests and wetlands can aid in maintaining a balance in climate conditions and nurturing environments for pollinators.
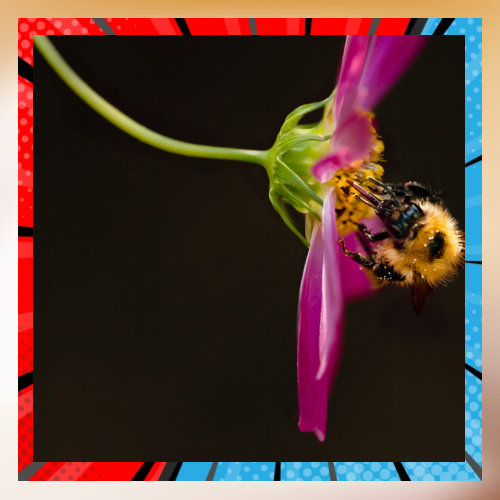
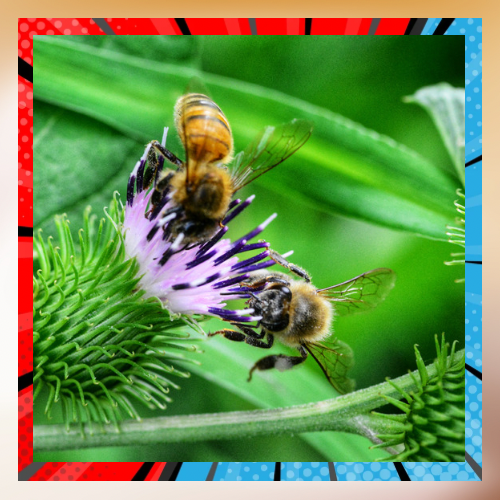


Observing. Continuous studies and regular monitoring play a role in comprehending the condition of pollinator populations and evaluating the impact of conservation efforts. Involving the public through citizen science initiatives to observe pollinator behavior not yields data but also enhances awareness about the significance of pollinators. Moreover, scientific investigations offer perspectives into the habits well being and relationships of pollinators within their habitats thus guiding conservation approaches.
Advocating for policies. Influencing decision makers. We must establish laws and rules to safeguard pollinators at levels—local community levels, up to the global scale—including measures such as prohibiting or limiting the usage of harmful chemicals in agriculture and promoting sustainable farming methods while preserving natural environments like habitats untouched by human activity. Advocacy initiatives play a role in educating policymakers and the general public about the role of pollinators and the necessary steps to ensure their protection.
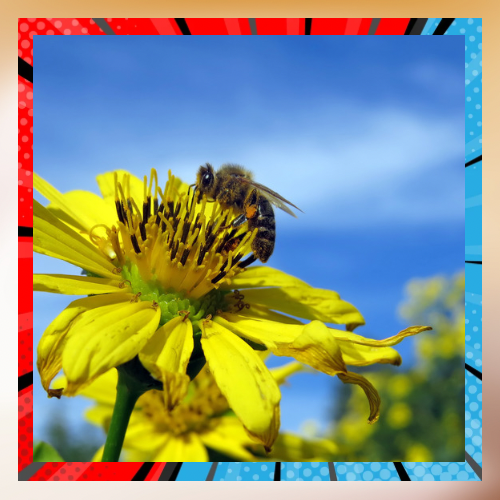
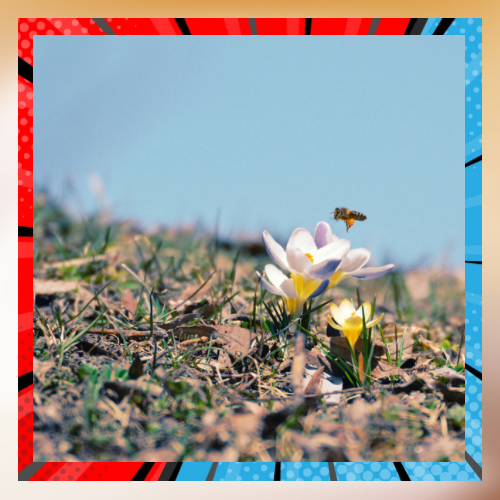


In closing.
Pollinators are crucial for the well being of ecosystems and the efficiency of farming activities.They have an impact in preserving biodiversity and ensuring food security while playing their part in the processes that sustain life on our planet. However, pollinators are facing challenges stemming from factors like loss of habitats, chemicals used in agriculture, effects of climate change, and diseases. By restoring habitats introducing farming practices tackling climate change issues and supporting research and policy endeavors it is possible to safeguard and nurture pollinators making sure they thrive and carry out their roles effectively. The well being of these creatures plays a role, in shaping the future of our food systems and natural surroundings.
References:
1. National Geographic – Pollinators. https://www.nationalgeographic.org/society/protect-our-pollinators/
2. World Wildlife Fund – Pollinators. https://www.worldwildlife.org/pages/the-beauty-and-benefits-of-bees-and-other-pollinators
3. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations – Pollinators. https://www.fao.org/pollination/en
4. United States Department of Agriculture – Pollinators. https://www.usda.gov/pollinators